Electrocardiogram: Understanding the Heart Through ECG
The human heart is one of the most vital organs in the body, pumping blood and oxygen to sustain life. Monitoring its activity is essential to prevent and detect heart conditions early. One of the most widely used diagnostic tools in cardiology is the Electrocardiogram (ECG). This test has become a cornerstone in modern healthcare, helping millions of people every year understand their heart health.
In this article, we will explore what an electrocardiogram is, how it works, why it’s important, and how costs differ across countries—highlighting why Turkey is one of the most affordable and reliable places to get an ECG.
What Is an Electrocardiogram?
An Electrocardiogram, often shortened as ECG, is a simple, painless, and non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart. Every heartbeat generates an electrical signal that travels through the heart muscle. An ECG captures these signals and presents them as waveforms on a screen or paper.
Doctors analyze these waveforms to detect heart rhythm, rate, and potential abnormalities such as arrhythmias, ischemia, or previous heart attacks.
How Does an ECG Work?
An ECG uses electrodes attached to the skin, typically on the chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes pick up tiny electrical impulses produced by the heart. The signals are transmitted to an ECG machine, which records them.
The results are displayed as a series of waves:
- P wave – Represents atrial contraction.
- QRS complex – Represents ventricular contraction.
- T wave – Represents ventricular recovery.
By analyzing these waves, cardiologists can identify whether the heart is functioning normally or showing signs of disease.
Types of Electrocardiogram Tests
There are different types of Electrocardiogram tests, each serving a specific purpose:
- Resting ECG : This is the standard ECG performed while the patient is lying down. It lasts only a few minutes and provides a snapshot of heart activity at rest.
- Stress ECG (Exercise ECG) : Also known as a treadmill test, this involves recording the heart’s activity while the patient exercises. It helps detect problems that only appear during physical activity.
- Holter Monitor (24-48 hour ECG) : This is a portable device worn by the patient for continuous monitoring, usually over 24 to 48 hours. It detects intermittent issues such as irregular heartbeats.
- Event Monitor : Similar to the Holter monitor but used over a longer period (weeks or months). It is activated when symptoms occur.
- Telemetry ECG : Used in hospitals to continuously monitor patients, especially those in critical care.
Why Is Electrocardiogram Important?
The ECG plays a critical role in heart health for several reasons:
- Early Detection of Heart Disease – Identifies heart attacks, arrhythmias, and other conditions before they worsen.
- Monitoring Chronic Conditions – Helps patients with ongoing heart disease manage their health.
- Guiding Treatment – Doctors use ECG results to adjust medications or recommend procedures.
- Prevention – Even healthy individuals may undergo ECG as part of routine check-ups, especially if they have risk factors.
Common Conditions Detected by ECG
An Electrocardiogram can reveal a wide range of heart-related problems, including:
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart enlargement (hypertrophy)
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Conduction abnormalities
Who Should Get an ECG?
While not everyone needs frequent ECGs, certain individuals benefit more from the test:
- Patients with chest pain or palpitations
- Individuals with family history of heart disease
- People with high blood pressure or diabetes
- Smokers or individuals with high cholesterol
- Athletes undergoing health screenings
- Patients preparing for surgery
Electrocardiogram vs. Other Heart Tests
An ECG is often the first test performed because it is fast, affordable, and non-invasive. However, it is sometimes combined with other diagnostic tools for a complete picture:
| Test | Purpose | Invasiveness | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrocardiogram | Records electrical activity of heart | Non-invasive | Minutes |
| Echocardiogram | Uses ultrasound to view heart structure | Non-invasive | 30–60 min |
| Cardiac MRI | Provides detailed imaging | Non-invasive | 60+ min |
| Angiography | Visualizes blood vessels | Invasive | 1–2 hrs |
The ECG remains the most accessible and commonly used test because it is simple, safe, and cost-effective.
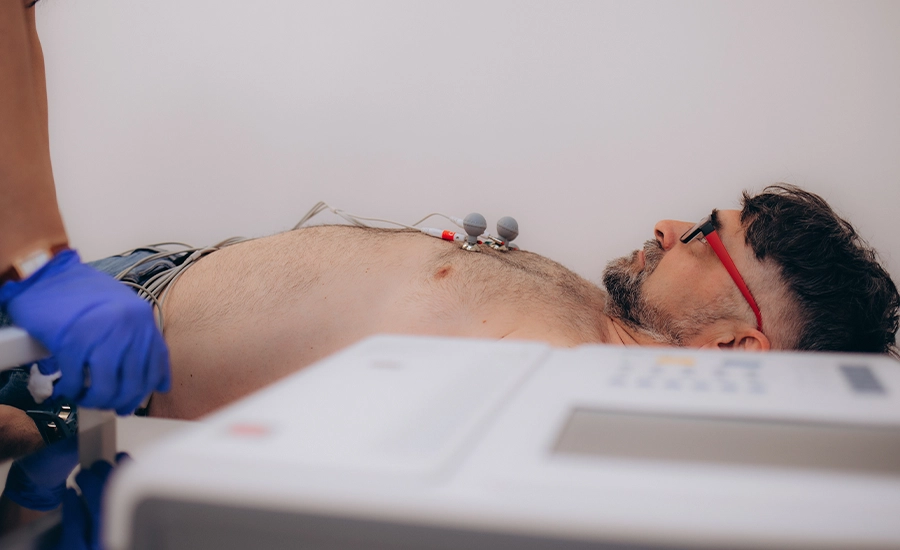
Cost of Electrocardiogram in Different Countries
The cost of an Electrocardiogram (ECG) varies widely across the world. In the United States and parts of Europe, prices are often much higher compared to Turkey, which has become a hub for affordable and high-quality healthcare services.
Here is a comparison:
| Country | Average Price for ECG (USD) |
|---|---|
| United States | $100 – $250 |
| Germany | $80 – $150 |
| United Kingdom | $70 – $120 |
| Turkey | $20 – $50 |
As the table shows, Turkey consistently offers the most affordable prices without compromising quality.
Why Turkey Is a Top Destination for ECG and Heart Health Services
- Affordable Healthcare Costs – Patients save up to 70% compared to Western countries.
- Advanced Technology – Hospitals and clinics in Turkey use modern ECG equipment.
- Expert Cardiologists – Highly trained professionals provide world-class care.
- Medical Tourism Growth – Turkey is recognized internationally for medical excellence and affordability.
How to Prepare for an ECG
Preparation for an Electrocardiogram is simple:
- Wear comfortable clothing that allows access to your chest area.
- Avoid applying creams or lotions on the skin before the test.
- Inform your doctor about medications, as some may affect the results.
- Stay calm—stress and anxiety can sometimes alter heart rhythm.
Risks and Limitations of ECG
While the Electrocardiogram is very safe, there are a few limitations:
- It may not detect all heart problems, especially if they occur intermittently.
- Stress tests or continuous monitoring may be required for accurate diagnosis.
- The accuracy depends on proper placement of electrodes and interpretation by professionals.
Future of ECG Technology
The future of Electrocardiogram testing is moving towards:
- Wearable ECG Devices – Smartwatches and fitness trackers already include ECG features.
- AI-Powered Analysis – Artificial intelligence improves diagnostic accuracy.
- Remote Monitoring – Patients can be observed continuously at home.
- Integration with Telemedicine – ECG data can be shared instantly with doctors worldwide.
The Electrocardiogram (ECG) is one of the most important and accessible tools in modern medicine. It provides invaluable insights into the heart’s electrical activity, helping detect conditions early, guide treatments, and save lives.
Whether you need a quick check-up or ongoing monitoring, an ECG is fast, painless, and affordable. While many countries charge high fees for this test, Turkey offers world-class cardiology services at a fraction of the price, making it a leading destination for patients around the globe.
Taking care of your heart begins with awareness, and the Electrocardiogram is a simple yet powerful way to ensure your heart is beating strong and healthy.